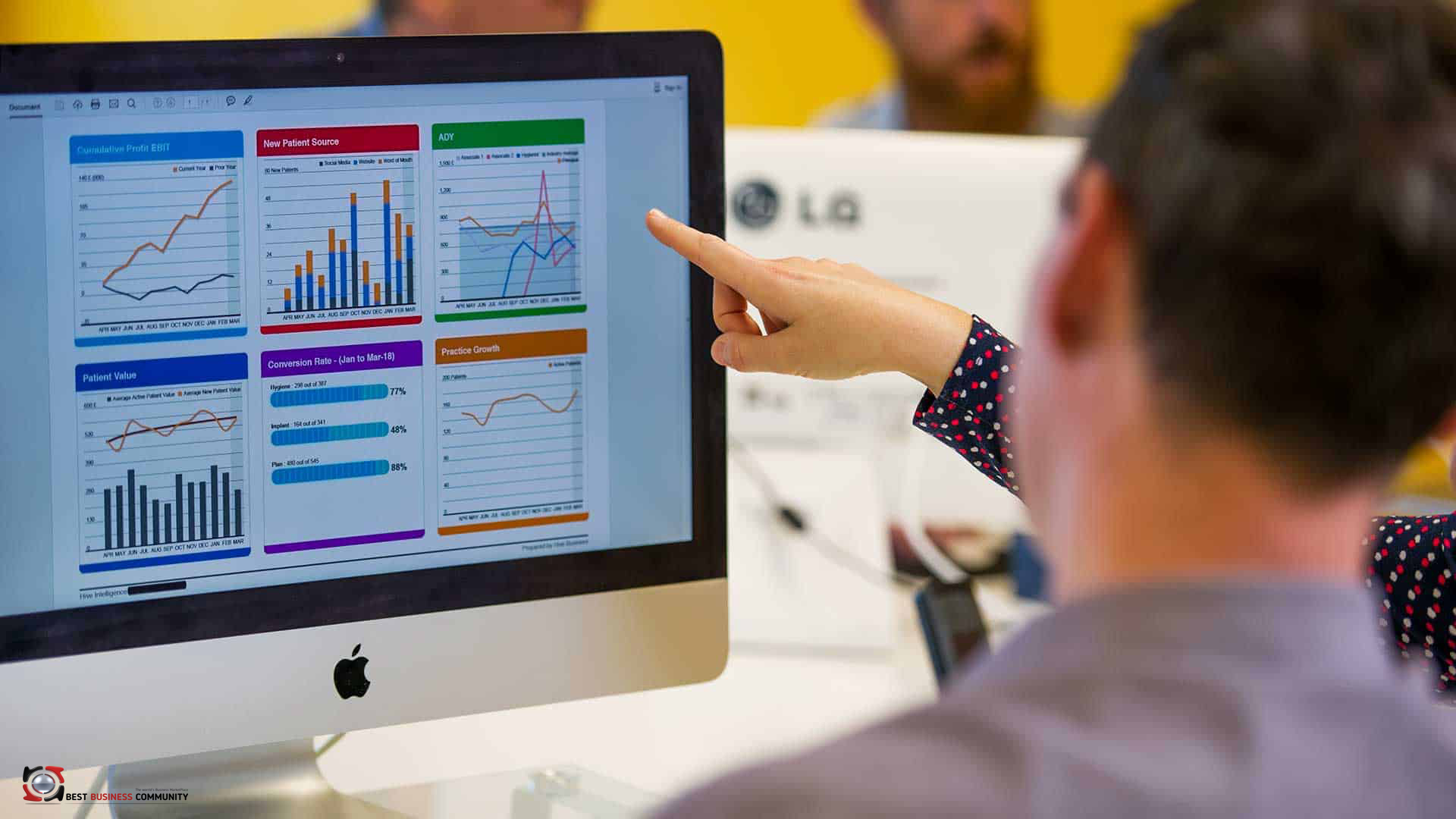
Understand what EBIT is and how it works?
Just like Net profit after tax (NPAT), there are not important numbers than Earnings Before net Interest and Tax (EBIT). It is surprising that there are a number of companies list on exchanges around the world.
It does not make money and often they are of little interest to investors. EBIT is calculate by taking the earnings (before significant items and extraordinary items) before net interest has been deduct. Before the income tax obligation on earnings has been deduct. Net interest is the total interest paid on borrowings (or borrowing costs) minus any interest received on money deposited. The EBIT can sometimes be found in the statement of financial performance (previously known as Profit and Loss Statement). Although many companies will just list one figure for earnings before tax and this will include significant items. EBIT Margin is another measure investors can use to assess financial health of a company.
EBIT Margin:
The EBIT Margin shows you the percentage of each dollar of sales revenue that is left after all expenses have been removed, excluding net interest and income tax expenses. As the EBIT Margin differs markedly between different industries it is important that this is take into account when comparing companies. Retail companies expect to have quite small EBIT Margin as they rely on small margins accompanied with high sales volume. Other industries would have far smaller sales volume but expect to offset that with much higher profit margins. All of these different factors directly impact on the EBIT Margin. Unlike many fundamental pieces of data, it is possible to consider the EBIT in isolation, and it often is. However, it can be combine with other data to form more detail picture. It just looked at on its own as general trend.

What is EBITDA?
EBITDA: earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Depreciation = non-cash expense of the wear and tear on fixed assets based on the respective useful lives. Amortization = non-cash expense of writing off intangible assets over their useful lives. EBITDA is often use to compare the profit potential between companies because it allows a fair comparison. Note however, that EBITDA does not accurately reflect a company’s ability to generate cash and should not use to replace the term “cash flow”. One of the greatest strengths of successful companies is the ability to generate profits. They also provide above average returns to shareholders and many investors. These investments help to earn profit before interest. You can make money with these investments. There are lots of people who are investing in such type of investments. We provide you top quality of information about such type of services.
Profitability: Profitability % = EBIT / SALES measurement represents the operating performance of a business expressed as a return on sales. It also provides a measurement of operational efficiency in the profit and loss account, void of finance costs. It always gives you profit when you are getting your earning before tax and interest.